Limb development timeline:
- Starts in: 4th week (Upper limb initiated 3-4 days before and stays ahead of the lower limb)
- Finished by: 8th week
![]()
Limb Buds initiation:
- Limb bud is mesenchyme covered by ectoderm (end of 4th week)
- Source of limb components:
- Lateral plate mesoderm/LPM (somatic)→bone, connective tissue, vasculature
- Paraxial mesoderm (somite-derived)→muscle (myotome)
- Neural tube: motor and sensory neurons
- Surface ectoderm: epidermis
- Neural crest: melanocytes
- Structure & formation of limbbuds:
-
- Form from somatic lateral plate mesoderm
- Edge of bud the apical ectodermal ridge (AER)→critical for limb formation
- Within the limb bud are the progress zone (high proliferation) and the mesenchymal mesoderm (stop dividing, differentiate into proper proximal/distal fate)
- Molecular limb embryology:
-
- Intermediate mesoderm→ FGF8 (mitogen)→ ↑ LPM to proliferate→ Induces Limb bud
- FGF8→initiates Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER)
- AER releases FGF8→ stimulates growth in progress zone→ controls where the limb forms along the A/P axis of the body
- Limb axes: Limb axes are unusual: anterior (thumb), dorsal (back of the hand), distal (fingers)
| Development of the three limb axes | |
|
|
| 2. Anterior/Posterior Axis |
|
| 3. Dorsal/Ventral Axis |
|
- The pattern signaling of Shh, Wnt-7a, and FGF are codependent and integrated
- Forelimb/hindlimb:
-
- Leg expresses: Pitx1 and Tbx4 txn factors (controlled by Hox-c genes)
- Arm expresses: Tbx5 which inhibits Tbx4
- Digits formation:
- AER delineates where digits will form.
- ZPA & SHH determine which digits will form & where.
- The webbing of finger and toes removed by apoptosis induced by BMP
- Limb bud malformations often related to urogenital malformations: both involve intermediate mesoderm defects.
![]()
Bone Formation
- Cells differentiate first furthest from AER
- Endochondral ossification: Mesenchyme differentiates→ cartilage→ bone
- Lateral plate mesoderm condenses along long axis→ cartilaginous perichondrium→ replaced by bone
- Interzones between bones: differentiation into joint tissue
![]()
- Ossification:
- Diaphyses ossified by birth (begins at 7th week)
- Epiphyses shortly thereafter
- Continued bone growth occurs at the epiphyseal growth plate
Muscle formation
- Connective tissues dictate the pattern of muscle formation by passively guiding the direction of migration of muscle precursor cells
- 6th week: connective tissue guides the migration of muscle cell precursors from somite to limb bud → forming dorsal/ventral condensations
- Mesodermal Condensations differentiate into →myoblasts (muscle precursors)
- Dorsal and ventral muscle masses differentiate
| Dorsal muscle mass | Ventral muscle mass | |
| 1. Nerve supply |
|
|
| 2. Upper limb |
|
|
| 3. Lower Limb |
|
|
Rotation of limbs
- The upper limb rotates 90° laterally
- The lower limb rotates 90° medially
![]()
Limbs innervation
| Upper limbs | Lower limbs |
|
|
|
|
- Dorsal branches innervate dorsal muscle mass; ventral branches innervate ventral muscle mass
- Axon growth guidance by mesenchyme controls the final pattern of innervation
- Postganglionic sympathetic fibers use developing vasculature as a guide
- Sensory axons develop later (slower) via sympathetic and motor axons as a guide
![]()
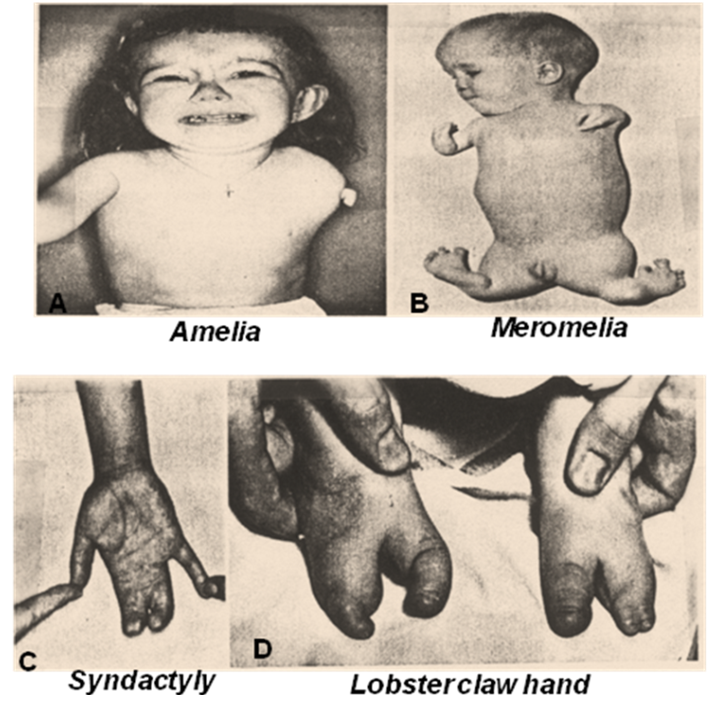
Congenital limb defects (developmental defects):
| 1. Amelia |
|
| 2. Meromelia |
|
| 3. Phocomelia |
|
| 4. Ectrodactyly |
|
| 5. Polydactyly |
|
| 6. Syndactyly |
|
| 7. Mirror Image Duplications |
|
Also read:
Also Watch:
- Embryology -Limb Development from the Youtube channel “DocvTV”
- Introduction to Limb Development from the Youtube channel “Kate Lee“
- Apical Ectodermal Ridge, zone polarizing Activity from the Youtube channel “Nabil Ebraheim”